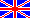
Plant |
Family | Rutaceae |
English |
Angostura, Angostura tree, Cusparia bark tree? |
Latin |
Angostura trifoliata (Willd.) T.S.Elias, Cusparia angostura (Rich.) A.Lyons, Cusparia officinalis Engl., Galipea officinalis J.Hancock, Angostura trifoliata, Cusparia angostura (Spreng.) A. Lyons, Cusparia febrifuga Humb., Cusparia officinalis (Willd.) Engl., Galipea cusparia, Galipea officinalis J. Hancock |
Plantparts | Bark, Unspecified |
|
Ungrouped Diseases & Uses |
Abdominal trouble, Aids digestion, Anti-diarrheic, Antidiarrhetic, Anti-diarrhoeal, Antidiarrhoeic, Anti-fatigue, Antifebrile, Anti-pyretic, Antispasmodic, aperient, bad digestion, benificial effect on the digestion, Bitter, Bitter Tonic, catharic, Cathartic, Chlorosis, cholagogic, Cholagogue, complaints of the stomach, Convalescence, convulsive state, cramp, cramps, diaorrhea, Diarrhea, Diarrhoea, Digestive, Digestive stimulant, digestive trouble, Digestive weakness, disease of the stomach, dispepsia, Dyspepsia, Emetic, Eupeptic, exhaustion, Expellant of bile, faintness, Fatigue, Febrifugal, febrifuge, Febrile response, feebleness, fever, feverish condition, Fevers, Gastropathy, Good for digestion, good for the stomach, improves digestion, Indigestion, induce vomiting, Languidness, Languor, Lassitude, laxative, Listlessness, movements of the bowel, Nausea, Pick-me-up, Poor digestion, Promotes digestion, Psychostimulants, Pungent, purgative, Pyretic, Pyrexia, reduce fevers, relax spasms, relieves fevers, spasm, Spasmolytic, stimulant, Stimulants, stimulates digestion, stimulating, Stomach aliment, stomach atony, stomach complaints, stomach debility, Stomach disease, stomach disorders, Stomachic, stomach lassitude, stomach problems, stomach tonic, Stomach trouble, tiredness, Used as a stimulant, vomitive, Warming digestive, weakness, weak stomach, weariness |
TCM - Traditional Chinese medicine |
TCM MERIDIAN: NA, Traditional Chinese medicine, Used in traditional Chinese medicin |
Local (Geographical) use |
Phytomedical use in Brazil |
Ingredients |
| | alkaloid, Bitter Components, Cadinene, cyanidin, essential oil, glycoside, L-Cadinene, pinene, vitamin |
|
|